Do you experience pain when drinking something hot or cold?
Do you hate brushing because it’s uncomfortable?
If you answered yes, you probably have sensitive teeth.
So how do get sensitive teeth?

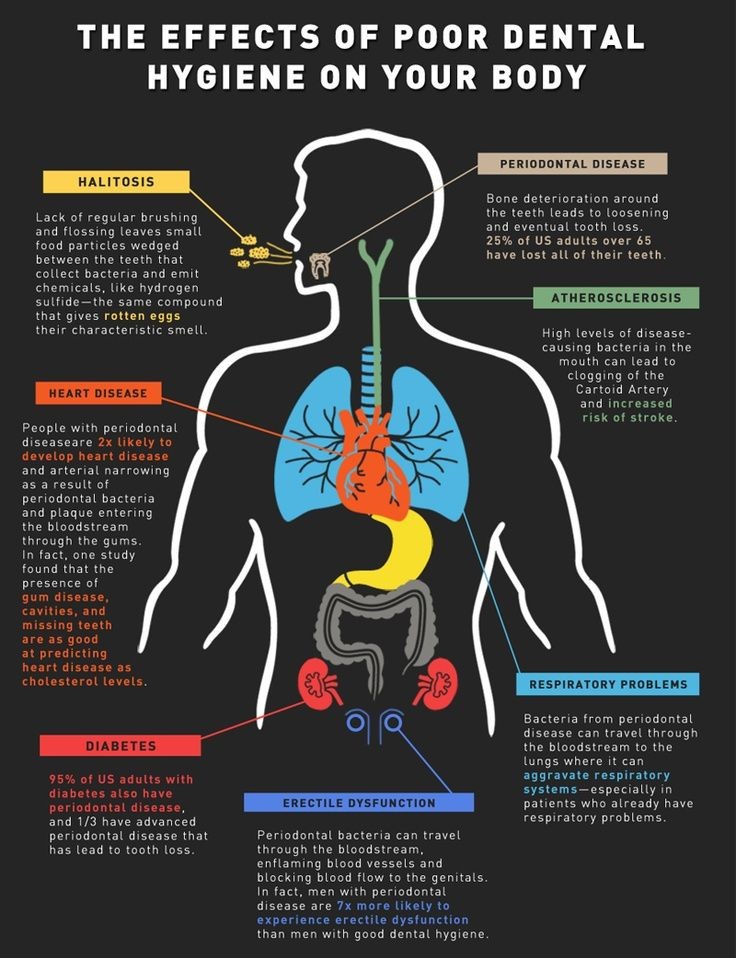
Tooth sensitivity happens because of exposed dentin due to enamel loss or receding gums. Dentin is the grayish or yellowish tissue that is found under your enamel and contains a large number of tubes. These tubes run from the tooth’s outer surface to the nerve, and when exposed are highly sensitive to temperature changes. That’s why eating specific foods (such as hot, cold or spicy) may be painful.
Causes for tooth sensitivity can include:
- Brushing too hard – Aggressive brushing can wear away your tooth enamel and gum line, exposing your roots
- Cracked teeth – A cracked tooth can expose your dentin and make your tooth vulnerable to bacterial plaque, inflaming your nerves
- Grinding your teeth – Continuous teeth grinding can wear down enamel and uncover your dentin
- Gum disease – Gum disease can cause pain as your teeth break down and gums recede
- Tooth bleaching – Teeth bleaching products that contain peroxide or baking soda can irritate exposed roots or dentin
- Age – People who are between the ages of 25 to 30 years old are more susceptible to sensitive teeth
How to tell if you have sensitive teeth
The best way to see if you have sensitive teeth is by visiting your dentist. Your dentist will check for exposed dentin and try to determine what the cause is. If your tooth sensitivity is due to cavities, they can be treated. If it’s due to gum disease, a comprehensive cleaning can be done to remove plaque and tartar. However, if the cause is due to exposed dentin, there are a number of treatment options available to reduce sensitivity.
In office treatments
- Fluoride varnishes can be applied to seal tubule openings and rebuild exposed dentin and worn away enamel
- Fluoride gels or foams can be placed in a disposable tray covering your teeth. As you bite down on it for a few minutes, it provides a high dosage of fluoride to strengthen your teeth
- Bonding agents can be used to seal exposed dentin and reduce tooth sensitivity
At home treatments
- Use a soft bristle toothbrush which can minimize the erosion caused from brushing too hard
- Use toothpaste with potassium nitrate, which penetrates exposed dentin and soothes painful tooth nerve endings
- Brush with a high concentration fluoride toothpaste that can strengthen your teeth and help protect them from pain
- Brushing gently and ensuring you don’t over brush
Tooth sensitivity is unpleasant and can be a sign of more serious oral problems. If you’re experiencing tooth sensitivity, definitely seek out professional dental help. The dental professionals at the Lotus Dental Group are experienced at treating a wide variety of dental issues and take patient care seriously. Contact us today at (669) 222-8315 if you’re having problems with your teeth.